Room 810, 8F, No. 780, Cailun Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai, China.
Puheng Biomedicine (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Puheng Biomedicine (Shanghai) Co., Ltd is an innovative enterprise focused on the research and development and application of novel in vitro 3D organ/disease models, including complex 3D models such as NAC-Organ, organoids, organ-on-a-chip, etc. The company's independently developed NAC-Organ technology is the world's first assembly-based in vitro 3D model construction and culture technique based on nano-nucleic acid materials, capable of rapidly achieving high-throughput, standardized production of humanized complex organ/disease models. The company has established modeling techniques for common chronic diseases with chronic liver disease as a characteristic, various tumors, important physiological organs...
-
Development of in vitro 3D complex disease models
-
Drug screening based on in vitro 3D models
-
Development of Regenerative medicine technology
Leading technological innovation and industrial transformation
-
NAC-linker is a Cell junction material developed by PUHENG Technology based on Synthetic biology technology.It enables efficient self-assembly of cells in a three-dimensional space and allows precise control over cell types, quantities, and spatial distri
-
Our NAC-Organ technology allows for the preparation of a 3D liver model (NAC-Liver) containing hepatocytes and non-parenchymal cells within 24 hours. NAC-Liver can be stably cultured in vitro for over 30 days, maintaining high levels of hepatocyte secreti
-
The automated cultivation system developed for NAC-organ enables high-throughput automated cultivation and testing of 3D models, ensuring standardization of the models and reproducibility of the test results. By utilizing high-content imaging systems, hig
News Center
重磅消息!美国疾病控制与预防中心的科学家已被告知逐步停止所有猴子研究!
近日,《科学》杂志披露的一则重磅消息在全球生物医学界引发巨大震动:美国疾病控制与预防中心(CDC)正被指示逐步停止所有猴子研究,涉及约200只用于艾滋病、肝炎等重大传染病研究的猕猴。如果计划落地,这将成为美国首次主动终止内部非人灵长类动物研究项目,标志着动物实验模式的历史性转折。事实上,早在今年7月,美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)便已宣布不再专门征集动物实验项目,并明确要求研究人员在设计动物研究时优先采用...
成果解读 | 新型核酸纳米载体实现对耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌的靶向及治疗
当前耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(MRSA)因滥用抗生素引发多重耐药,其携带的mecA基因编码的 PBP2a 蛋白可逃避 β-内酰胺类抗生素杀伤,导致肺炎、败血症等致命感染频发。全球范围内,MRSA 感染不仅延长患者住院时间、增加医疗成本,现有替代抗生素疗效还因耐药菌株进化持续下降,而新型抗生素研发停滞,临床治疗陷入严峻困境。 反义寡核苷酸(ASOs)虽可靶向mecA抑制 PBP2a表达,恢复 MRSA对β-内酰胺类抗...
成果解读 | 朴衡人源化MASH模型助力解析MASH 相关肝癌发生新机制
代谢功能障碍相关脂肪性肝病(MASLD,原非酒精性脂肪肝 NAFLD)全球发病率已达 20%-25%,其严重亚型代谢功能障碍相关脂肪性肝炎(MASH)是肝细胞癌(HCC)的重要诱因,目前约占全球肝癌病例的2%,预计2030年将成为肝癌的首要病因。 与HBV/HCV相关肝癌相比,MASH 相关肝癌具有独特的分子和免疫特征,脂质过载会引发氧化应激、复制应激及核苷酸库失衡,进而导致DNA损伤和突变积累,成为关键癌前事件...
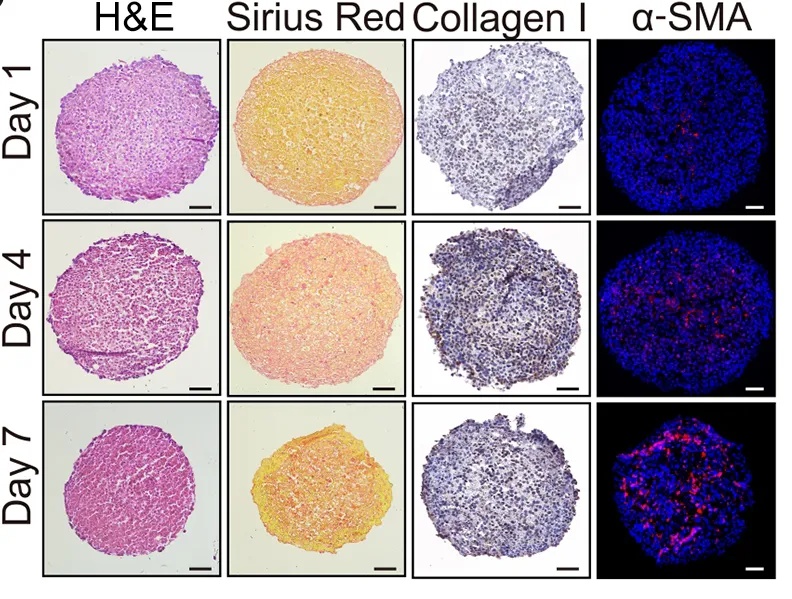
文献分享丨微流控构建的人工肝微组织用于急性肝衰竭修复
急性肝衰竭是一种危及生命的疾病,原位肝移植是最有效的治疗手段之一,但供体器官稀缺严重限制其临床应用。人工生物工程肝移植物移植成为替代方案,却面临三大核心挑战:功能性人肝细胞来源有限,人工肝移植物快速构建技术受限,移植后细胞存活能力差,难以实现长期治疗效果。 传统 3D 细胞聚集体(如细胞球状体模型)存在尺寸受限(氧和营养供应不足)、易形成坏死核心、长期培养稳定性差等问题,无法满足大规模组织工程需求。因...
产品介绍 | 朴衡博迈人源化3D肝纤维化模型
目前基于肝纤维化模型的病理及药物研究局限性较强,例如2D细胞培养过于简单,无法模拟肝非实质细胞与肝实质细胞在复杂三维空间中的相互作用。传统肝类器官3D模型通常细胞种类单一,缺乏关键免疫组分且难以主动诱导纤维化以用于疾病造模。动物模型周期长、种属差异大,其致病机制与人类临床存在差距。因此,能够整合多种细胞类型、高度模拟体内真实微环境的3D肝纤维化模型,将是精准研究疾病机制和药物筛选的理想工具。 朴衡博迈...
文献分享 | 基于类器官模型的肿瘤研究:乳酸通过表观遗传调控肿瘤干性和可塑性
在结直肠癌(colorectal cancer, CRC)中,肿瘤组织仍部分保留其起源组织的层级结构,包括肿瘤干细胞(cancer stem cells, CSCs)和肿瘤分化细胞(cancer differentiated cells, CDCs)。CSCs广泛存在,并可能对结直肠癌的进展具有重要贡献。既往研究在体内模型和体外类器官中均观察到层级细胞谱系(CSCs 与 CDCs)以及细胞可塑性现象,尽管它们对治疗耐药性和癌症复发具有显著影响,但其具体调控机制及生物学优...
成果解读 | 朴衡人源化3D肝模型精准验证肠源代谢物IPA逆转肝纤维化
近年来研究发现,肠道代谢物经门静脉系统进入肝脏后,可参与调控肝脏炎症反应与纤维化进程。这一机制为开发靶向“微生物-代谢物-免疫”交互作用的抗纤维化治疗策略提供了新的研究方向。以往基于肝纤维化的研究多依赖原代肝星状细胞和小鼠模型。其中原代肝星状细胞培养中表型不稳定,易去分化,并且难以模拟体内真实的复杂肝脏微环境。物种差异导致小鼠与人在肝脏免疫系统等方面存在显著不同,导致对纤维化可逆性的模拟并不理想。因...
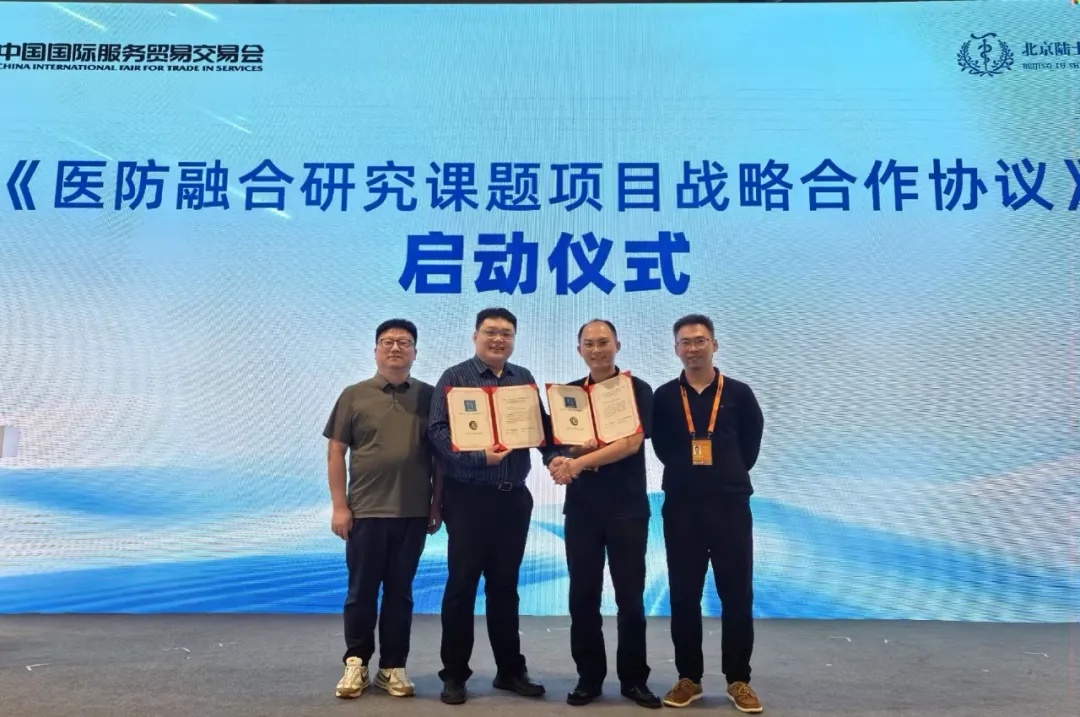
朴衡博迈与中科未来生物技术研究院签署战略合作协议——加速新一代再生治疗技术的临床转化应用
2025年9月14日,在北京首钢园举办的中国国际服务贸易交易会现场,朴衡博迈与中科未来生物技术研究院正式签署战略合作协议,双方将联合开展国家卫健委《医防融合研究课题》。本项目旨在通过我司新一代再生治疗技术在骨科领域的大规模临床应用研究,为建立我国标准化生物治疗体系提供大数据支持。
重磅消息!美国国立卫生研究院宣布停止资助纯动物研究!
2025年7月7日,美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)宣布,今后将不再专门征集涉及动物的研究项目提案。此前NIH已经多次明确鼓励研究人员设计涉及动物的项目,并于4月已经宣布了“优先考虑以人为本的研究技术”的倡议,并在与美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)联合主办的首届“减少动物试验研讨会”上进行了分享。新的 NIH 资助项目都应侧重于非动物方法的新兴方法学(New Approach Methodologies,NAM),这套现代替代方案包括包...